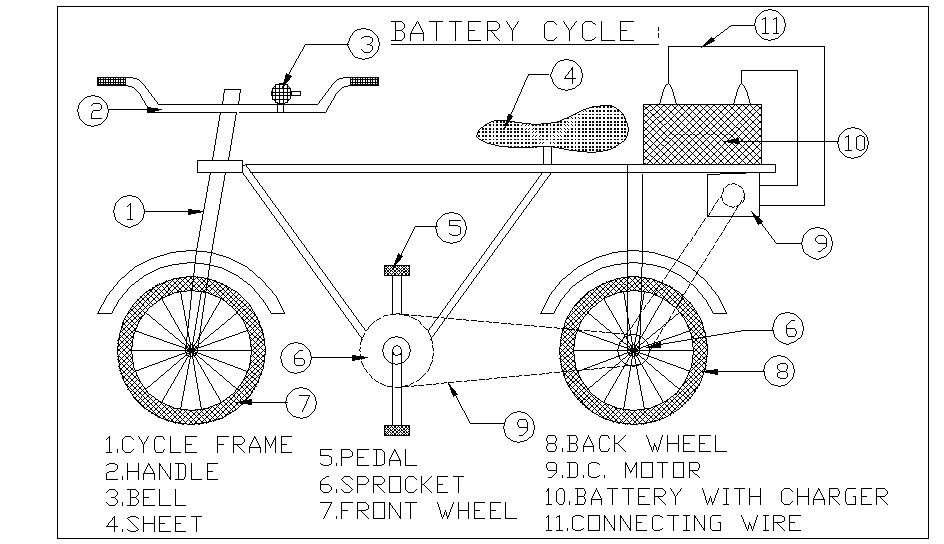
An electric bike is simply an upgraded version of a regular bike. You can also say a regular bike is the soul of an electric bike. Both of the bikes share almost the same components such as the frame, pedals, seat, handles, etc and also operates in the same way. The only major difference is the electric bike comes with some added electrical components.
The electrical components help gives you to assist while climbing up the hill or whenever you need extra speed resulting in a better riding experience without much effort. The best part about an electric bike is when you ran out of power you can still use it like a regular bike by pedalling. So now before coming to the point on how an electric bike works, we will take a look at the history of electric bike and explore all the different types available.
History behind the Electric Bike
It is true that electric bikes have gained popularity only in the recent few years but If you think that the electric bike is a recent innovation then you are wrong. A lot of people have filed patents for electrical components of the e-bike since the 1800s.
The first patent for the electric bike was filed long back in 1895 by Ogden Bolton Jr. It was invented 2 years later by Hosea W. Libbey. It came with two electric motors and batteries and was called ‘double electric motor’. Around 50 years later a new patent was granted to Jesse D. Tucker, he made a motor which allowed a wheel to freely move and use the other wheel as a gearing system.
Again, back in the 1990s torque motors and power controllers came into existence. A few years later Japan also filed a patent for another device which uses torque motors and power controller. In 2004, the production of electric bike hiked by 35% and it is to believe that e-bikes will capture at least 65% of the total bike market in the near future. So, this makes the electric bike a 120-year-old innovation.
What are the different types of electric bike?
E-bikes have been mainly classified into three major categories: Pedal assist, Pedal Only, and Electric only. Also, note that e-bikes can be still used by propelling by the rider just like a regular bike when it is out of battery so you can choose to not use the electrical components and still enjoy riding.
Pedal Assist e-bike – These are also known as Pedelec. Here the controller only activates the power when you start pedalling the bike. If you enjoy riding a normal bike then you should go for the pedal-assist e-bike only, why? The best thing I like about the pedal-assist bile is you don’t have to hold the throttle for so long in a certain position and focus more on pedalling.
You also have further settings to control the assist. For example, low pedal assist, medium pedal assists, and high pedal assist. As you only have to pedal, with high assist setting it will give you much more range as compared to the throttle mode e-bike.
Throttle mode e-bike – These are also known as electric-only e-bikes. This kind of e-bike works just like a motorbike or a scooter. It makes the bike ride itself and you just have to apply little effort.
Whenever you use the throttle the controller pumps the power to the motor and helps move the bike forward. Most of the e-bikes in the US comes with the throttle feature and it allows you to enjoy your free ride while in some other countries these throttle mode e-bikes are strictly not allowed and you have to use pedal-assist e-bikes.
This option also drains the battery much faster and in some countries like the UK you have a speed limit which restricts you from going beyond 15 miles per hour.
All the components of an Electric Bike
E-bikes have most of the components the same as a regular bike. The electrical components here include the battery, the motor, the controller, and the throttle. All these components are made to work with each other and thus getting a prebuilt e-bikes makes it difficult for upgradability. You can also build an e-bike from scratch but make sure to check the components if they are compatible with each other. Now let’s talk about some of the main components of an e-bike in brief.
Motor
The motor is the main component of an e-bike. It helps give extra power to the bike. The more powerful the motor will be, the faster you will ride. When buying an electric bike in uk, you should check on how powerful a motor is. It is generally determined by the voltage. A normal electric bike has motor ranging from 30 V to 52 V.
A powerful motor will also drain your battery much faster. There are three types of motor available based on their placement on the e-bike – Front motor, Rear Motor, and the Mid-Motor. The front or rear-mounted motor system is also called the Hub Motor System while the Mid-Motor is known as Mid-Drive System.
Front Motor – The front motor is fixed on the front tire of the e-bike. It comes with fixed gear and generally offers only 1 speed. These are best for flat grounds and definitely not suitable for climbing. While the motor is on the front wheel it will feel like you have been pushed and it gives you a clean riding experience whereas sometimes it may not feel natural and you will have a hard time pushing the bike.
Mid-Motor – Mid motor system or Mid-drive system is located at the middle of the bike along with the pedal. These bikes feel natural and are well balanced as the motor is mounted at its centre of gravity. You will feel like you are riding a regular bike without additional weight and pressure. Mountain bikes include a mid-drive system because this kind of system is best for climbing hills and they are also great for flat ground as well. The mid-motor system comes with various gears and speed to control from.
Rear Motor – The rear motor e-bike has the motor mounted on its rear wheel. These also come with a fixed gear and single speed. Again, these are also not great for climbing hills as the whole weight is on the rear wheel. These are great when you are riding on flat ground. While using the rear motor system you will feel like you have been pushed forward.
Battery
E-bikes are powered by the battery and it is the most expensive part of an e-bike. The price of an e-bike generally depends on the quality of the battery it comes with. E-bikes come with Lithium-ion batteries and these are best in terms of quality and longevity. Some other kinds of e-bikes include Nicads LA and NiMH batteries. The battery power is measured in wattage and you will get something ranging from 200 watts and goes up to 600 watts. Depending upon the battery capacity an e-bike can go an average of 50 Kilometres to a maximum of 80 Kilometres.
Charging e-bikes batteries is also very easy. You just have to plug in the charger into any electrical socket and just wait for it fully charge. Some batteries come with a fast charging and self-cooling feature but it all depends on how much you pay for it.
How does an electric bike works?
Electric bikes have been made to make your riding experience even better. As a regular bike maximizes your power by 5 times, the e-bike will further double that power giving you a much more range without applying much pressure. Working of an e-bike is really simple and works just like a motorbike. Some e-bikes allow you to control the power by the help of throttle (Throttle Mode) while other e-bikes pump the power only when you pedal it (Pedal Assist).
The controller basically consists of the throttle and the gears.
The throttle is actually located in the handlebar of the e-bike just like a motorcycle which allows you to control the motor. Along with the throttle you have volume dial which allows you to select the gears. Once you twist the throttle it gives power to the motor and the bike pushes forward. E-bikes also include a digital display letting you know the speed and battery you are left with.
Final Words
So, this was how do electric bikes work. All the different types of electric bikes available in the market will work a bit differently based on their design. The only common things are the battery and motor which all e-bikes required to make it function. So, should you buy an e-bike? Well definitely Yes! You should definitely go for an e-bike for a better riding experience and hopefully, this article was useful to you understanding how an electric bike works and all of its different components responsible for it.